Contents
Structure and Function of the CPU: Exploring the Intricacies
In this post, we will delve deep into the inner workings of the CPU, examining Structure and Function of the CPU, to carry out the myriad tasks that we entrust to our computers.
In the world of modern computing, the CPU, or Central Processing Unit, stands as the heart and soul of every computer system. Often referred to as the “brain” of the computer, the Structure and Function of the CPU are central to the entire computing experience.
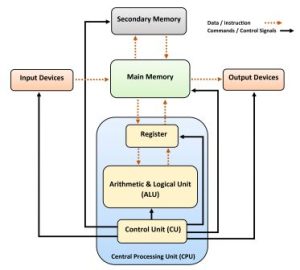
image source : commons.wikimedia.org
It plays a pivotal role in executing instructions and performing calculations, making it a fundamental component of any digital device.
Structure and Function of the CPU
Understanding the CPU’s Role
Before we delve into the intricacies of the Structure and Function of the CPU, it’s essential to grasp its overarching role in a computer system. The CPU is the primary component responsible for executing instructions, performing calculations, and managing data within a computer. It acts as the bridge between software and hardware, translating high-level programming instructions into low-level machine language that the computer can understand and execute.

Structure of the CPU
The Structure and Function of the CPU are closely intertwined, as the CPU’s design directly impacts how it carries out its functions efficiently. Let’s start by breaking down the key structural components of the CPU.
- Control Unit (CU):
The Control Unit is like the conductor of an orchestra, directing the flow of data and instructions within the CPU. It interprets program instructions, fetches data from memory, and coordinates the execution of instructions. The CU also manages the flow of data between various components of the CPU and other peripherals.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU):
The Arithmetic Logic Unit is the mathematical powerhouse of the CPU. It handles arithmetic and logical operations, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and comparison. When you perform calculations or make decisions in software, the ALU is responsible for carrying out these tasks at the hardware level.
- Registers:
Registers are small, high-speed memory units within the CPU that store data temporarily while it is being processed. These registers include the Program Counter (PC), which keeps track of the current instruction being executed, and the Accumulator, used for storing intermediate results during calculations.
- Cache Memory:
Cache memory is a small, ultra-fast memory unit that stores frequently used data and instructions. It acts as a buffer between the CPU and main memory (RAM), reducing the time it takes to access data. Cache memory comes in different levels (L1, L2, L3), with L1 being the closest and fastest, and L3 being the largest but slower.
- Clock Speed:
The CPU’s clock speed, measured in Hertz (Hz) or Gigahertz (GHz), determines how many instructions it can execute per second. A higher clock speed generally results in faster processing, but other factors, such as architecture and efficiency, also play a crucial role.

Function of the CPU
With a basic understanding of the Structure and Function of the CPU, let’s delve into how these components work together to carry out the core functions of a computer.
- Fetch:
The CPU initiates its operation by fetching program instructions from the computer’s memory, often referred to as RAM. The Control Unit (CU) takes charge of this process. It uses the Program Counter (PC) to keep track of the address of the next instruction to be fetched. The instruction is then loaded into the Instruction Register for further processing.
- Decode:
Once the instruction is fetched, it needs to be decoded. The Control Unit interprets the instruction to determine what operation needs to be performed and which data or registers will be involved. This step is essential for understanding the Structure and Function of the CPU because it guides the subsequent actions.
- Execute:
After decoding the instruction, the CPU moves to the execution phase. Here, the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) takes center stage. The ALU performs the actual computation or operation specified by the instruction. For example, if the instruction is to add two numbers, the ALU will add the values stored in the designated registers or memory locations.
- Writeback:
The final step in the CPU’s operation is the writeback phase. Once the instruction is executed, the results are stored back in memory or registers as needed. This ensures that any changes made during the execution are preserved for future use.
The Fetch-Decode-Execute cycle is the fundamental process that the CPU repeats continuously to execute programs and perform tasks. It’s crucial to note that the CPU can execute millions or even billions of these cycles per second, depending on its clock speed and architecture, highlighting the incredible speed and efficiency of modern CPUs.
Instruction Sets and CPU Architecture
The Structure and Function of the CPU also depend on the CPU’s architecture and instruction set. An instruction set is a collection of machine-level instructions that the CPU can understand and execute. Different CPUs have different instruction sets, which can impact their capabilities and compatibility with software.
Two common CPU architectures are:
CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computer):
CISC CPUs are designed with a large and diverse instruction set. They can perform complex operations with a single instruction, which can be advantageous for certain tasks but can also lead to slower clock speeds. Intel x86 processors are classic examples of CISC architecture.
RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer):
RISC CPUs, on the other hand, have a simpler and more streamlined instruction set. They typically execute instructions in a single clock cycle, resulting in faster processing. ARM processors, commonly used in mobile devices, follow the RISC architecture.
The choice of CPU architecture can impact a computer’s performance, power efficiency, and compatibility with software. Some CPUs even employ a combination of CISC and RISC features to strike a balance between complexity and speed.
Parallelism and Multicore CPUs
In recent years, the Structure and Function of the CPU have evolved to include parallelism and multicore processing, allowing for even greater performance and efficiency.
Parallelism involves executing multiple instructions or tasks simultaneously, rather than sequentially. CPUs achieve parallelism through various techniques, such as pipelining and superscalar architecture. These approaches enable the CPU to overlap the fetch, decode, and execute stages of multiple instructions, leading to improved throughput and speed.
Multicore CPUs take parallelism to the next level by integrating multiple CPU cores onto a single chip. Each core functions as an independent CPU, capable of executing its own set of instructions.
This design dramatically enhances a computer’s multitasking capabilities, as multiple cores can work on different tasks simultaneously. Whether you’re running complex simulations, editing multimedia, or playing video games, multicore CPUs offer a significant boost in performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Structure and Function of the CPU are integral to the operation of every computer system. The CPU’s architecture, components, and instruction sets collectively determine its performance, efficiency, and compatibility with software.
From the Fetch-Decode-Execute cycle to the emergence of parallelism and multicore processing, CPUs continue to evolve, pushing the boundaries of what computers can achieve.
As technology advances, CPUs will likely continue to become more powerful and energy-efficient, enabling us to tackle increasingly complex tasks. Whether you’re using a smartphone, laptop, or a powerful desktop computer, the Structure and Function of the CPU remain at the core of your computing experience, ensuring that your digital world runs smoothly and efficiently.
Friends, you have just read the post “ Structure and Function of the CPU: Exploring the Intricacies ” we hope you will like this post. If yes then share it with your friends and keep visiting our website for more such posts.
If you interested to read about Astrology & Hindu Religion : Click here
……………………………
Technological Tips
Also Read : Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EPROM): Unveiling the Digital Archives- 7 important Applications
Also Read : Cloning HDD: Your Ultimate Guide to Data Migration and Backup- with 5 valuable tips
Also Read : What is RAM , Why it is called RAM ? How does RAM work ?
Also Read : Fundamental of Computer: Understanding the Basics in Simple Terms-14 Important facts
Also Read : Network Topologies: definition,types, classification,examples etc-A Comprehensive Guide
Also Read : Database Management System (DBMS) in detail with it’s definition,types, classification,examples
Also Read : What is Bus in Computer Systems: Understanding Its Role in Data Transfer
Also Read : Computer Memory: An Introduction to Storing and Retrieving Data
Health & Wellness
Also Read : Heavy Periods after Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms, and Management are explained in detail
Also Read : Women’s Reproductive Health: Empowering Women through Knowledge and Care
Also Read : Fatty Lower Abdomen No More: Secrets to a Trim and Toned Waistline
Travel India
Also Read : Swaminarayan Akshardham Temple New Delhi- A Complete A to Z Tour Guide
Also Read : Exploring the Golden Triangle in India: A Journey Through History and Culture
Also Read : Best Travel Agencies in India: Exploring the Perfect Journeys : Top 5
( you were reading What is Binary representation of data-easy explanation in 11 steps )

