Contents
Network Topologies: definition,types, classification,examples etc- A Comprehensive Guide
Network Topologies refers to the arrangement or layout of devices and connections in a computer network. It defines how the devices in the network are physically or logically connected to each other.
Different network topologies have varying advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of topology depends on factors like scalability, fault tolerance, cost, and performance requirements.

image source : commons.wikimedia.org
Definition of Network topology
A network topology / network topologies defines the physical or logical structure of a computer networks, outlining how devices (such as computers, printers, routers, and switches) are interconnected and how data flows within the network / networks .
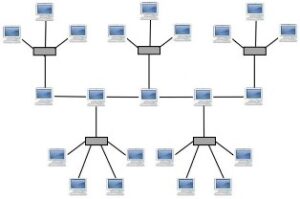
Types of Network Topologies

Bus Topology:
- Definition: In a bus topology, all devices are connected to a central communication line, known as the bus or backbone. Data travels along the bus and is received by all devices on the network. Each device checks the data’s destination address and accepts the data if it matches its own.
- Advantages: Simple to implement and cost-effective for small networks.
- Disadvantages: Prone to collisions and scalability limitations as more devices can lead to decreased performance.
- Uses: Bus topologies are suitable for small local area networks (LANs) with a limited number of devices.
- Example: Early Ethernet networks used a bus topology with coaxial cables.

Star Topology:
- Definition: In a star topology, all devices are directly connected to a central hub or switch. Data from one device is sent to the central hub, which then forwards it to the intended recipient.
- Advantages: Easy to manage, fault isolation (a failure in one device does not affect others), and scalability as new devices can be added without disrupting the network.
- Disadvantages: Dependence on the central hub; if it fails, the whole network can go down.
- Uses: Commonly used in home and office networks, where devices connect to a central router or switch.
- Example: Many modern Ethernet-based networks use a star topology.

Ring Topology:
- Definition: In a ring topology, devices are connected in a closed loop, where each device is connected to exactly two others, creating a circular pathway for data to travel.
- Advantages: Equal access to the network for all devices and efficient data transmission as data moves in one direction along the ring.
- Disadvantages: Difficult to reconfigure and susceptible to network disruption if one device or connection fails.
- Uses: Ring topologies are not as common as other topologies but can be found in specific networking setups.
- Example: Token Ring networks used a ring topology.

Mesh Topology:
- Definition: In a mesh topology, each device is connected to every other device, creating redundant paths for data to travel.
- Advantages: High redundancy and fault tolerance; if one link fails, data can find an alternate path.
- Disadvantages: High cost and complexity as the number of connections increases exponentially with the number of devices.
- Uses: Critical communication systems where reliability is crucial.
- Example: Some wide area networks (WANs) and large-scale data centers use a partial mesh topology.

Tree (Hierarchical) Topology:
- Definition: A tree topology combines multiple star topologies interconnected through a central bus. It forms a hierarchy of devices with the root node at the top.
- Advantages: Scalable and efficient for larger networks, providing a structured and organized layout.
- Disadvantages: Dependency on the root node; failure of the central hub can disrupt the entire network.
- Uses: Used in medium to large-sized enterprise networks to organize and manage interconnected LANs.
- Example: Complex corporate networks often utilize a tree topology.
Classification based on Physical and Logical Topologies
Physical topology refers to the actual physical layout of devices and cables in the network. Logical topology, on the other hand, describes the path that data follows as it travels between devices.
Examples:
- Physical Bus Topology: Devices connected along a single shared communication line.
- Logical Ring Topology: Data travels in a circular manner from one device to the next, although physically devices may not be connected in a ring layout.
- Hybrid Topology: Combination of two or more different network topologies (e.g., star-bus or star-ring).

- Fully Connected Mesh Topology: Every device is directly connected to every other device in the network, creating a fully redundant setup.
- Partially Connected Mesh Topology: Some devices are directly connected to every other device, while others have fewer direct connections.
Conclusion
Network topologies play a crucial role in determining the efficiency, scalability, and fault tolerance of a computer network. Each network topologies has its advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to carefully assess the network’s requirements before choosing the most appropriate topology for a specific application.
Friends, you have just read the post “ Network Topologies: definition,types, classification,examples etc-A Comprehensive Guide ” we hope you will like this post. If yes then share it with your friends and keep visiting our website for more such posts.
If you interested to read about Astrology & Hindu Religion : Click here
……………………………
Technological Tips
Also read : Find My RAM: A simple method to know RAM of Computer
Also read : Windows 11 vs Windows 10: A Comprehensive Comparison of the Two Operating Systems
Also read :How to Go Viral on Instagram Reels: A Guide to Capturing Attention
Also read :What is Bus in Computer Systems: Understanding Its Role in Data Transfer
Also read :Computer Memory: An Introduction to Storing and Retrieving Data
Also Read : What is Deep Learning, Key Concepts & Important 5 Applications of Deep Learning
Also Read : Google Cloud AI: Shaping the Future of Intelligent Applications
Health & Wellness
Also Read : Heavy Periods after Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms, and Management are explained in detail
Also Read : Women’s Reproductive Health: Empowering Women through Knowledge and Care
Also Read : Fatty Lower Abdomen No More: Secrets to a Trim and Toned Waistline
Travel India
Also Read : Swaminarayan Akshardham Temple New Delhi- A Complete A to Z Tour Guide
Also Read : Exploring the Golden Triangle in India: A Journey Through History and Culture
Also Read : Best Travel Agencies in India: Exploring the Perfect Journeys : Top 5
*you were reading Network Topologies: definition,types, classification,examples etc-A Comprehensive Guide*